Oracle
Introduction
Pair stores cumulative values as a sample for the following data:
- Active bin ID
- Volatility accumulated ()
- Number of bins crossed ()
The active bin ID can be easily converted into the bin price via helper functions, allowing users to obtain historical prices easily.
Using cumulative values allow us to take the time-weighted average values.
Samples
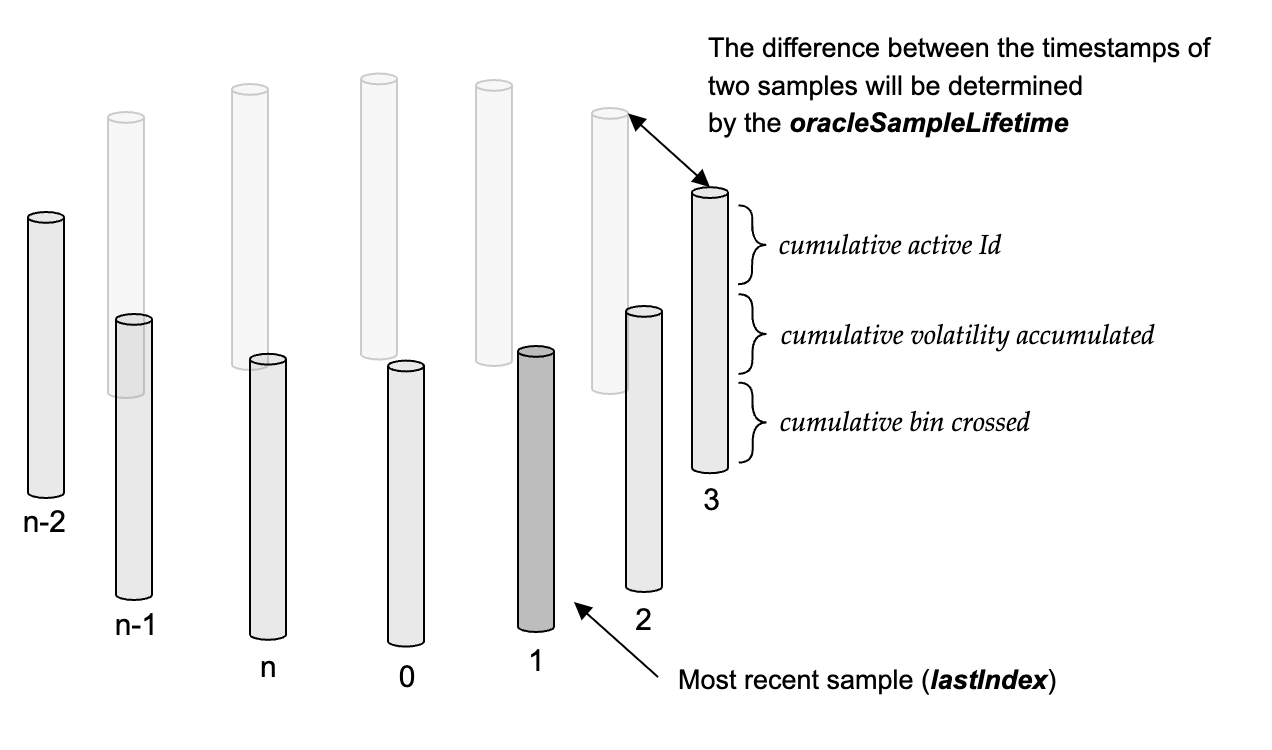
Samples are stored in a 16-bit circular array. However, by default, the oracle array only stores 2 samples, but it can be extended by anyone by calling increaseOracleLength. This is to shift the burden of gas cost to the oracle user.
Each sample consists of three values: cumulative bin ID, cumulative volatility accumulated and cumultive bins crossed.
Samples are updated at the end of each swap.
A new sample is created if enough time has passed since the creation of the previous sample as defined by the variable oracleSampleLifeTime. To be specific, given a new swap, if the time since creation of sample has exceeded oracleSampleLifeTime, then we create sample . Otherwise, we update the cumulative values in sample .
Time-Weighted Average Values
Sample values can be read by calling getOracleSampleFrom. This will return the three cumulative values at the time specified by the timeDelta input: cumulativeId, cumulativeVolatilityAccumulated and cumulativeBinCrossed.
To calculate the average value of any of those three variables, getOracleSampleFrom needs to called on two different timestamps, and the average value will be:
To convert time-weighted average ID to time-weighted average price, you can use the getPriceFromId() function from the Router contract.